Introduction
Is your IPTV infrastructure delivering the reliability and video quality modern viewers expect? Over 87% of viewers abandon streams due to buffering, latency, or poor encoding quality. Enter the PVI Encoder IPTV – a professional-grade IPTV hardware solution designed to address these critical pain points.
The global IPTV market is projected to reach $117.1 billion by 2027, growing at 18.1% annually. This explosive growth spans sports broadcasting, corporate communications, churches, and hotel entertainment systems.
Whether you’re an IPTV reseller, live sports broadcaster, or tech enthusiast, understanding what makes the PVI Encoder IPTV stand out is essential. This guide breaks down everything you need to know.
What Is PVI Encoder IPTV and Why It Matters
A PVI Encoder IPTV is a specialized hardware encoder that converts video signals from various sources (HDMI, SDI, or component) into IP-based streaming formats compatible with IPTV networks. Unlike consumer-grade encoders, PVI encoders are built for professional broadcasting environments where stability, quality, and reliability are non-negotiable. PVI Encoder IPTV.
At its core, an IPTV encoder performs video compression using advanced codecs like H.264 and H.265 (HEVC), transforming high-bandwidth raw video into efficient, streamable data packets. This compression is critical – it reduces bandwidth requirements by up to 50% while maintaining broadcast-quality video.
Why Professional IPTV Encoders Matter:
- Consistency: Consumer encoders often fail during extended broadcasts. Professional PVI encoders are engineered for 24/7 operation without degradation.
- Quality Control: Precise bitrate management, resolution control, and codec optimization ensure every frame meets broadcast standards.
- Protocol Support: Support for multiple streaming protocols (RTMP, UDP, HLS, RTP) enables compatibility with diverse platforms and delivery networks.
- Scalability: Hardware encoding offloads CPU-intensive tasks, allowing broadcasters to scale operations without proportional infrastructure costs. PVI Encoder IPTV.
The difference between consumer and professional encoding becomes evident in mission-critical scenarios: a church streaming Sunday services can’t afford mid-sermon dropouts, and a sports broadcaster losing connection during a championship game faces immediate audience loss and reputational damage. PVI Encoder IPTV.
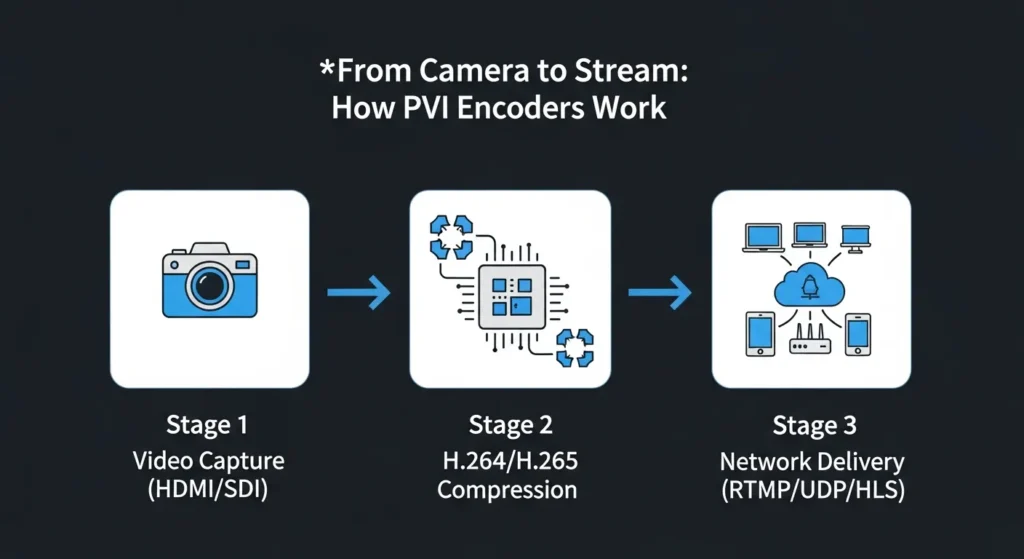
How PVI Encoder IPTV Works: A Simple Technical Overview
Understanding the workflow of a PVI Encoder IPTV helps broadcasters optimize their setup:
Stage 1: Video Capture – The encoder receives raw video through HDMI (consumer cameras) or SDI (professional equipment), supporting resolutions from 480p to 4K at up to 60fps.
Stage 2: Video Compression – Dedicated processing applies H.264 or H.265 compression, analyzing frame-to-frame changes and encoding only differences. A 1080p60 raw stream (3 Gbps) drops to 5-8 Mbps with H.264 – a 99.7% reduction. H.265 achieves similar quality at 3-5 Mbps.
Stage 3: Network Delivery – Compressed video is packetized and transmitted via Ethernet using configured protocols (RTMP, UDP, HLS). The network stack handles buffering, error correction, and adaptive bitrate switching for smooth delivery.
7 Powerful Benefits of Using PVI Encoder IPTV
Benefit 1: Ultra-Low Latency for Real-Time Broadcasting – PVI encoders achieve 0.5-1.5 seconds glass-to-glass latency with optimized protocols like SRT or UDP. Critical for sports, auctions, and remote production. Software encoders often introduce 3-8 seconds of delay.
Benefit 2: Rock-Solid Stability for 24/7 Operations – Industrial-grade components, redundant power supplies, and thermal management enable continuous operation. Field data shows 99.9% uptime – less than 9 hours downtime annually.
Benefit 3: Enterprise-Grade Video Quality – Adaptive bitrate control, advanced noise reduction, and 10-bit color depth support maintain consistent quality. Professional results preserve color accuracy and reduce compression artifacts. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Benefit 4: True Scalability Without Performance Loss – Hardware encoding is deterministic – performance doesn’t fluctuate. One encoder can simultaneously output multiple streams without quality degradation, serving both high-bandwidth and mobile viewers.
Benefit 5: Protocol Flexibility Across Platforms – Support for RTMP (social media), UDP (local distribution), HLS (mobile streaming), and RTSP (IP cameras) eliminates the need for multiple encoders or transcoding servers.
Benefit 6: Minimal Network Bandwidth Requirements – H.265 encoding reduces bandwidth 40-50% vs. H.264. A hotel distributing 20 HD channels can reduce requirements from 160 to 80 Mbps, avoiding costly infrastructure upgrades.
Benefit 7: Simple Setup and Maintenance – Web-based configuration guides users through 10-15 minute setup. No OS management, driver updates, or codec licensing. Firmware updates are rare and simple, making professional broadcasting accessible to smaller organizations.

Key Features That Make PVI Encoder IPTV an Ultimate Choice
Professional PVI encoders pack features that address real-world broadcasting challenges:
Multiple Input Options
HDMI inputs connect to consumer cameras, computers, and media players. SDI inputs interface with professional broadcast equipment, supporting long cable runs up to 300 feet without signal degradation. Some models include composite inputs for legacy equipment, ensuring compatibility across diverse production environments.
Advanced Codec Support
H.264 (AVC) remains the industry standard for compatibility, while H.265 (HEVC) delivers superior compression for bandwidth-constrained scenarios. Main Profile and High Profile encoding options allow broadcasters to balance quality and device compatibility. Some premium encoders also support AV1 and VP9 for cutting-edge efficiency.
Intelligent Bitrate Control
CBR (Constant Bitrate) ensures predictable network usage for fixed-bandwidth environments. VBR (Variable Bitrate) optimizes quality by allocating more bits to complex scenes and fewer to static content. ABR (Adaptive Bitrate) dynamically adjusts encoding based on network conditions, preventing buffer underruns. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Multi-Protocol Output Simultaneously
Output options include:
- RTMP/RTMPS: Push to YouTube, Facebook Live, Twitch, and custom RTMP servers
- UDP/RTP: Low-latency multicast for local IPTV distribution
- HLS: Adaptive streaming for mobile and web players
- RTSP: Integration with VLC, security systems, and custom players
- SRT: Secure, low-latency transmission over unpredictable networks
Industrial Reliability Features
Fanless designs eliminate mechanical failure points. Wide operating temperature ranges (0-50°C) ensure performance in uncontrolled environments. Watchdog timers automatically reset the encoder if software hangs occur. Dual Ethernet ports enable network redundancy, automatically switching to a backup connection if the primary fails.
Core Components of a PVI Encoder IPTV
Understanding encoder components helps in selecting the right model:
Video Input Interfaces
- HDMI: Supports resolutions up to 4K at 60fps, HDCP-compliant for protected content
- SDI: 3G-SDI supports 1080p60, 12G-SDI handles 4K60 for professional workflows
- Analog: Composite and component inputs for legacy equipment
Encoding Engine
Dedicated hardware encoding chips from manufacturers like Xilinx, Lattice, or proprietary ASICs provide consistent performance. These chips include hardware acceleration for motion estimation, the most CPU-intensive aspect of video compression. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Bitrate and Resolution Control
Configurable parameters include:
- Resolution: 480p to 4K output regardless of input resolution (upscaling/downscaling)
- Frame Rate: 15fps to 60fps with frame rate conversion
- Bitrate: 100 Kbps to 50+ Mbps depending on encoder model
Streaming Output Formats
Output is delivered via Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps) in containerized formats like TS (Transport Stream) for broadcasting, MP4 for recording, or FLV for RTMP streaming.
Beginner vs Enterprise Configurations
Beginner setups typically use single-input encoders with HDMI connectivity, H.264 encoding, and RTMP output – perfect for streaming to social media or a single IPTV server. Enterprise configurations feature dual/quad input encoders with SDI, H.265 encoding, multi-protocol simultaneous output, and redundant networking for mission-critical applications like television studios or large venue broadcasting. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Setup Time & Efficiency
Time is money in broadcasting. PVI encoders are engineered for rapid deployment:
Physical Setup: 2-3 Minutes
Connect the video source via HDMI or SDI cable, plug in Ethernet, and apply power. Most encoders include PoE (Power over Ethernet) support, eliminating separate power supplies.
Network Configuration: 3-5 Minutes
Access the web interface via the encoder’s default IP address or discovery software. Configure DHCP for automatic addressing or set a static IP for permanent installations. Most encoders include configuration wizards that auto-detect optimal settings.
Stream Configuration: 5-7 Minutes
Select the output protocol (RTMP, UDP, HLS), enter the destination server URL or multicast address, choose the codec (H.264/H.265), set bitrate and resolution, and click ‘Start Streaming.’ Total time from unboxing to live: 10-15 minutes.
Comparison with Software Encoders
Software encoders like OBS Studio or vMix require installing an operating system, installing the software, configuring capture cards, managing codec licenses, and troubleshooting driver conflicts. This process can take hours for beginners and requires ongoing maintenance. Hardware encoders eliminate these complexities, offering appliance-like simplicity that reduces training requirements and accelerates deployments.
Step-by-Step PVI Encoder IPTV Setup Guide
Step 1: Connect Your Video Source
Connect your camera, computer, or media player to the encoder using an HDMI or SDI cable. Ensure the source is outputting a resolution supported by the encoder (check specifications). For HDMI sources, disable HDCP protection in the source device settings if possible, as some encoders cannot encode protected content.
Pro Tip: Use high-quality shielded cables for runs over 15 feet to prevent signal degradation and electromagnetic interference. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Step 2: Configure Network Settings
Connect the encoder to your network via Ethernet. Access the web interface by typing the default IP address (usually printed on the device label) into a browser. Navigate to Network Settings and either enable DHCP for automatic IP assignment or configure a static IP address if your IPTV infrastructure requires fixed addresses.
Pro Tip: Assign static IP addresses in production environments to prevent address conflicts and simplify firewall rules.

Step 3: Set Your Streaming Destination
Choose your output protocol and enter the destination details:
- For YouTube: Select RTMP, enter rtmp://a.rtmp.youtube.com/live2/, and paste your stream key from YouTube Studio
- For Local IPTV: Select UDP, enter the multicast address (e.g., 239.255.0.1:5000)
- For VLC Playback: Select RTSP, note the generated URL (e.g., rtsp://encoder-ip:554/stream)
Pro Tip: Enable simultaneous multi-protocol output to stream to YouTube and your local server concurrently without additional hardware.
Step 4: Optimize Bitrate & Resolution
Match your output resolution to your source content – don’t upscale 720p to 1080p, as it increases file size without improving quality. Set bitrate based on available bandwidth:
- 720p30: 2-4 Mbps (H.264) or 1.5-3 Mbps (H.265)
- 1080p30: 4-6 Mbps (H.264) or 3-4 Mbps (H.265)
- 1080p60: 6-8 Mbps (H.264) or 4-6 Mbps (H.265)
Pro Tip: Test your upload bandwidth and set encoding bitrate to 80% of available bandwidth to account for network overhead and fluctuations. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Step 5: Go Live
Click ‘Start Streaming’ or ‘Start Encoding’ in the web interface. The encoder immediately begins transmitting. Verify the stream by opening your destination platform or playing the RTSP URL in VLC. Monitor the encoder’s status page for bitrate statistics, dropped frames, and network errors. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Pro Tip: Save your configuration as a preset for instant deployment of future streams with identical settings.
Performance & Streaming Quality Benchmarks
Professional PVI encoders deliver measurable performance advantages:
| Specification | Typical Performance |
| Maximum Resolution | 1080p @ 60fps (entry-level), 4K @ 60fps (premium) |
| Bitrate Range | 100 Kbps to 50 Mbps (model-dependent) |
| Glass-to-Glass Latency | 0.5-2 seconds (protocol-dependent) |
| Supported Protocols | RTMP, RTMPS, UDP, RTP, HLS, RTSP, SRT |
| Codec Support | H.264 (AVC), H.265 (HEVC), AAC/MP3 audio |
| Continuous Operation | 24/7 rated (99.9% uptime typical) |
| Power Consumption | 5-15W (varies by model and load) |
These benchmarks represent typical professional-grade encoders. Entry-level models may have lower maximum resolutions or bitrates, while premium models support 4K encoding and higher bitrate ceilings.
Real-world testing shows hardware encoders maintaining stable quality during 72-hour continuous broadcasts, with frame drop rates under 0.01% on properly configured networks. Software encoders, by contrast, often show gradual quality degradation due to memory leaks, thermal throttling, and background process interference.
PVI Encoder IPTV vs Traditional Encoding Solutions
Choosing between hardware and software encoding depends on your specific requirements:
| Factor | Hardware (PVI Encoder) | Software (OBS/vMix) |
| Stability | Excellent (99.9% uptime) | Good (depends on OS/hardware) |
| Initial Cost | Higher ($500-$5,000+) | Lower (Free-$1,200) |
| Scalability | Excellent (deterministic) | Limited (CPU-dependent) |
| Latency | 0.5-2 seconds | 3-8 seconds |
| Setup Time | 10-15 minutes | 1-4 hours (for beginners) |
| Maintenance | Minimal (firmware updates) | Regular (OS, drivers, software) |
| Best For | 24/7 operations, critical apps | Occasional streams, tight budgets |
When PVI Encoder IPTV Is the Better Choice:
- 24/7 broadcasting requiring maximum uptime
- Mission-critical applications where failure means revenue loss
- Installations in remote locations with limited technical support
- Environments requiring deterministic, predictable performance
- Scenarios where low latency (under 2 seconds) is essential
Better Alternatives & Add-Ons
Enhance your PVI encoder setup with these upgrades:
H.265 Encoding Upgrades
If your current encoder supports only H.264, upgrading to H.265-capable hardware reduces bandwidth by 40-50% or improves quality at the same bitrate. This is particularly valuable for 4K streaming or bandwidth-constrained networks. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Dual-Stream Encoders
Process two independent video sources simultaneously. Ideal for multi-camera productions, picture-in-picture setups, or broadcasting separate content to different destinations from a single device.
External Audio Modules
Professional XLR audio inputs and processing. Essential for churches, concerts, and corporate events where audio quality matches or exceeds video importance. Look for modules supporting audio delay adjustment to sync with video processing latency.
Solutions for Specific Industries:
- Churches: Look for encoders with NDI input support for integration with church production systems, automatic recording features, and multi-site streaming capabilities
- Sports/Events: SRT protocol support for reliable transmission over cellular networks, instant replay buffer storage, and multi-camera switching
- Esports: Ultra-low-latency configurations under 500ms, support for 1080p60 or 4K streaming, and integration with gaming overlay software
- IPTV Resellers: Rackmount multi-channel encoders processing 8-16 sources in 1U-2U chassis, centralized management interfaces, and redundant power supplies
Deployment Use Cases
IPTV Resellers Running 24/7 Channels – A European IPTV provider uses 16-channel encoders to distribute regional content to 50,000 subscribers. H.265 encoding reduces backbone bandwidth from 960 to 480 Mbps, saving €15,000 monthly. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Live Sports Broadcasting – A college athletics department streams 200+ events annually with sub-10-minute setup time. SRT protocol ensures stable transmission from unreliable venues. Total investment: $2,500 per encoder vs. $50,000+ for broadcast trucks.
Church Streaming Services – A 3,000-member church streams to YouTube, Facebook, and their website simultaneously. Automated recording stores services to NAS. Investment recovered in six months versus hiring professional services.
Hotel IPTV Systems – A 200-room resort converts satellite feeds to IP using PVI encoders, distributing via existing Ethernet. Eliminates RF amplifiers and set-top boxes. System paid for itself in 18 months through reduced maintenance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake 1: Wrong Protocol Selection
Using RTMP for local distribution introduces unnecessary latency and server load. UDP multicast is purpose-built for efficient one-to-many transmission within a local network. Conversely, don’t use UDP across the internet – it lacks error correction and will produce artifacts on unreliable connections. Use SRT or RTMP for internet transmission.
Fix: Match protocol to use case – UDP/multicast for local, RTMP/SRT for internet, HLS for mobile.
Mistake 2: Excessive Bitrate Configuration
Setting 1080p bitrate to 20 Mbps doesn’t improve quality beyond 8-10 Mbps – it only wastes bandwidth and excludes viewers with slower connections. Worse, if upload bandwidth can’t sustain the configured bitrate, the encoder drops frames, creating stuttering playback. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Fix: Test upload speeds and configure bitrate to 70-80% of available bandwidth. Use platform-specific guidelines (YouTube recommends 4-6 Mbps for 1080p30).
Mistake 3: Ignoring Firmware Updates
Manufacturers release firmware updates addressing bugs, adding protocol support, and improving encoding efficiency. Running outdated firmware means missing performance improvements and potential security vulnerabilities.
Fix: Check for updates quarterly. Schedule updates during maintenance windows, not during live events.
Mistake 4: Poor Network Planning
Placing encoders on congested network segments or behind underpowered routers causes packet loss and stream degradation. Broadcasting 1080p over WiFi is particularly problematic – wireless interference creates unpredictable bandwidth fluctuations.
Fix: Always use wired Gigabit Ethernet for encoder connectivity. Implement QoS rules prioritizing streaming traffic. For critical applications, use dedicated VLANs isolating broadcast traffic from general network usage.
Maintenance & Long-Term Storage Tips
Cleaning and Airflow
Even fanless encoders require periodic cleaning. Dust accumulation on ventilation slots restricts airflow, causing thermal throttling. Use compressed air every 3-6 months to clear vents. For rack-mounted units in dusty environments, consider blanking panels and positive-pressure enclosures. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Proper Storage Conditions
Store unused encoders in climate-controlled environments. Extreme temperatures and humidity damage electronic components over time. Use anti-static bags and original packaging when possible. Before deployment after extended storage, power on and run for 2-4 hours to stabilize components.
Firmware Update Schedule
Establish a quarterly firmware review process. Read release notes carefully – some updates require configuration resets. Always backup current configuration before updating. Test updates on non-critical encoders before deploying to production systems.
Configuration Backups
Export configuration files monthly and store off-device. This enables rapid recovery after hardware failures or accidental misconfigurations. Modern encoders support configuration upload, reducing reconfiguration time from hours to minutes. Label backups with date, location, and purpose for easy identification.
Final Verdict: Is PVI Encoder IPTV Worth the Investment?
For anyone serious about IPTV broadcasting – whether running a commercial service, streaming corporate events, or building a church media ministry – a professional PVI Encoder IPTV delivers unmatched reliability, quality, and simplicity. The combination of 24/7 stability, low-latency performance, and multi-protocol flexibility makes it the backbone of successful streaming infrastructure.
While initial costs exceed software solutions, the total cost of ownership favors hardware encoding: no recurring software licenses, minimal maintenance requirements, and deterministic performance that eliminates expensive troubleshooting. For mission-critical applications, the difference between 99% and 99.9% uptime isn’t academic – it’s the difference between satisfied viewers and lost revenue. PVI Encoder IPTV.

Ready to upgrade your IPTV broadcast? Try a PVI Encoder IPTV today for smoother, more reliable streaming.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between an IPTV encoder and an IPTV transcoder?
An encoder converts uncompressed video (from cameras, computers) into compressed streaming formats. A transcoder converts already-compressed video from one format to another (e.g., H.264 to H.265, or changing resolution/bitrate). Encoders are used at the source for live production, while transcoders optimize existing streams for different delivery contexts or devices.
Q2: Can PVI Encoder IPTV stream to multiple platforms simultaneously?
Yes, most professional PVI encoders support simultaneous multi-protocol output. You can stream to YouTube (RTMP), Facebook (RTMPS), your local IPTV server (UDP), and record to a NAS (RTSP) from a single encoder. Check your specific model’s specifications – entry-level units may support 2-3 simultaneous outputs, while enterprise models handle 10+. PVI Encoder IPTV.
Q3: Does PVI Encoder IPTV support 4K streaming?
4K support varies by model. Entry-level PVI encoders typically max out at 1080p60, which is sufficient for most applications and keeps bandwidth requirements manageable. Mid-range and premium models support 4K30 and 4K60 encoding with H.265, though this requires significantly more bandwidth (15-25 Mbps for 4K30, 25-40 Mbps for 4K60). Ensure your network infrastructure can handle these data rates before investing in 4K encoding.

