Introduction
Is your IPTV streaming setup delivering the quality, stability, and scalability modern viewers expect? In an era where the global IPTV market is projected to reach $194.21 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 17.8%, the IPTV Encoder Box has emerged as the cornerstone of professional broadcasting infrastructure. Whether you’re experiencing constant buffering, unacceptable latency issues, or inconsistent encoding quality, understanding the power of a dedicated IPTV Encoder Box can transform your entire streaming operation.
From IPTV resellers managing multiple 24/7 channels to churches broadcasting weekly services, hotels delivering in-room entertainment, and live event producers streaming sports tournaments, the IPTV Encoder Box addresses critical pain points that software-based solutions simply cannot match. This comprehensive guide reveals seven power secrets that will elevate your streaming performance to professional broadcast standards.
What Is an IPTV Encoder Box and Why It Matters
An IPTV Encoder Box is a specialized hardware device that converts raw video signals from cameras, SDI sources, or HDMI outputs into compressed, IP-based streaming formats suitable for broadcast over internet protocol television networks. Unlike software encoders running on general-purpose computers, these dedicated encoder boxes are purpose-built for video compression and transmission.
At its core, the IPTV Encoder Box performs real-time video compression using advanced codecs like H.264 and H.265 (HEVC), dramatically reducing file sizes while maintaining broadcast-quality visuals. The device takes uncompressed video input through interfaces such as HDMI, SDI, or composite AV, processes it through specialized encoding chips, and outputs network-ready streams via Ethernet connections.
The critical distinction between hardware and software encoding lies in dedicated processing power. Hardware IPTV encoder devices feature application-specific integrated circuits designed exclusively for video compression tasks. This specialization delivers consistent performance under heavy load, lower latency streaming typically 1-3 seconds versus 5-15 seconds for software, reliable 24/7 operation with industrial-grade components, reduced power consumption, and plug-and-play simplicity.
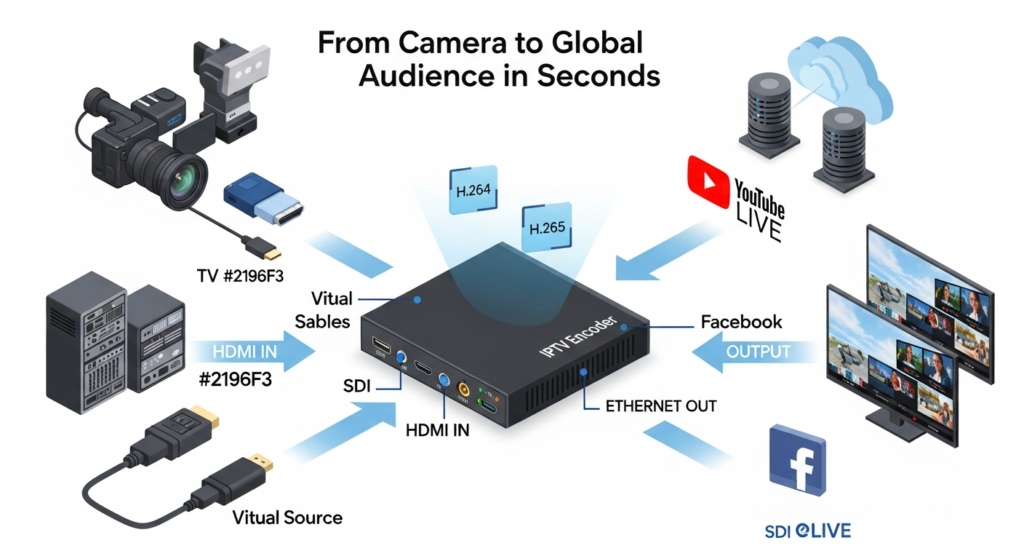
Core Components of an IPTV Encoder Box
Understanding the internal architecture of an IPTV Encoder Box empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions. Professional encoder boxes support multiple input standards including HDMI for consumer cameras and gaming consoles, SDI for broadcast-grade connectivity with superior signal integrity over long cable runs, and legacy composite AV inputs ensuring compatibility with older equipment.
The codec determines compression efficiency and stream compatibility. H.264 encoder technology remains the industry standard, offering universal playback support across devices with excellent quality at moderate bitrates. H.265 (HEVC) delivers 40-50% better compression efficiency, making it ideal for 4K streaming and bandwidth-constrained scenarios. Enterprise-grade IPTV hardware often supports both codecs.
Advanced encoder boxes provide granular bitrate control through Constant Bitrate (CBR) which maintains consistent data output essential for live broadcasting, and Variable Bitrate (VBR) which adjusts compression dynamically based on scene complexity. Modern IPTV transcoder boxes support multiple output protocols including RTMP for platforms like YouTube and Facebook Live, UDP and RTP for multicast streaming, HLS for adaptive bitrate delivery, and SRT for low-latency transmission with built-in error correction.
Recommended Options:
Beginners: Single HDMI input, H.264 encoding, RTMP output ($150-$300). SMBs: Dual inputs, H.264/H.265 support, multiple protocols, 1080p60 ($400-$800). Enterprise: Multi-channel, 4K support, API integration ($1,200-$3,500).
Setup Time & Efficiency with IPTV Encoder Box
One compelling advantage of an IPTV Encoder Box is operational efficiency. From unboxing to broadcasting your first live stream, a properly configured encoder requires approximately 8-12 minutes: physical connections and power-up (2 minutes), network configuration (3-4 minutes), stream destination setup (2-3 minutes), and video quality optimization (2-3 minutes). First-time users should allocate 20-25 minutes.
Network setup is straightforward with DHCP auto-configuration completing in under 30 seconds. Static IP assignment takes only 2-3 minutes when you have network parameters prepared. Software encoding solutions introduce significant complexity—installing applications, configuring sources, adjusting settings, and troubleshooting driver issues can require 30-90 minutes initially plus ongoing maintenance.
Consider a church broadcasting weekly services. With an IPTV Encoder Box, volunteers arrive 15 minutes early, power on the encoder which connects automatically to pre-configured destinations, verify audio and video, and begin broadcasting with a single button press. Total preparation: under 5 minutes. Software encoding requires booting a computer, launching software, configuring interfaces, and monitoring throughout—adding 15-20 minutes and requiring constant attention.
Step-by-Step IPTV Encoder Box Setup Guide
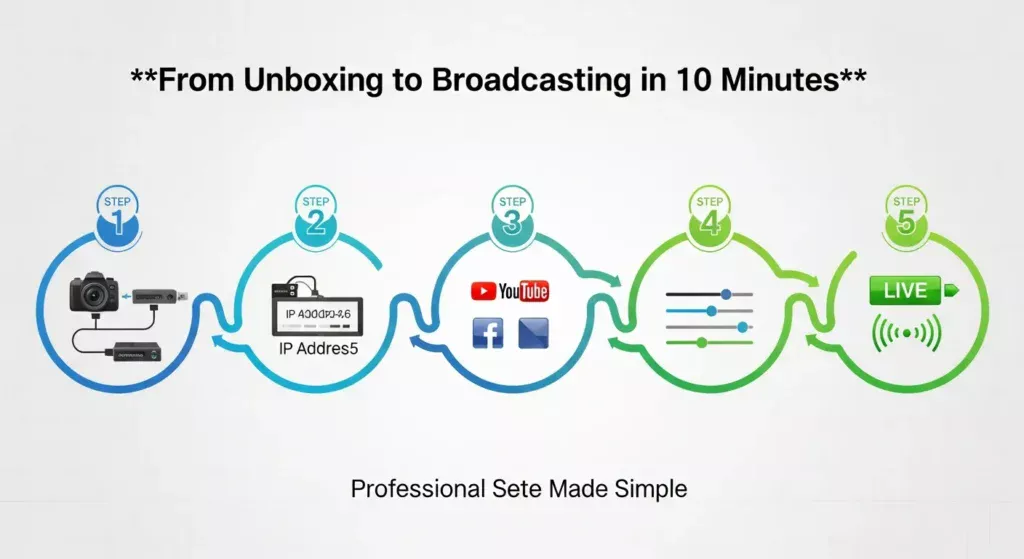
Step 1: Connect Your Video Source
Connect your camera or video source to the encoder’s input port. For HDMI connections, use high-quality cables—standard cables work for 1080p, but 4K requires Premium High Speed certification. Keep HDMI runs under 15 feet; for longer distances, use active cables or fiber optic extenders. SDI connections offer superior reliability for professional installations with BNC connectors maintaining signal integrity across 300 feet for HD-SDI.
Pro Tip: Power on your video source before connecting to the encoder. Many encoders auto-detect input resolution during initial connection, and hot-plugging can cause detection failures.
Step 2: Configure Network & IP Settings
Connect the encoder’s Ethernet port to your network using Cat5e or Cat6 cable. Most encoders ship with DHCP enabled, automatically obtaining an IP address. Locate the encoder’s IP by checking your router’s DHCP client list or using the manufacturer’s discovery tool. Access the web interface by entering the IP address into your browser.
For production environments, assign a static IP to prevent address changes from disrupting streams. Navigate to network settings, disable DHCP, and enter IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS servers.
Pro Tip: Reserve the encoder’s MAC address in your DHCP server for consistent IP assignment. Configure Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize encoder traffic during network congestion.
Step 3: Choose Stream Destination
Modern IPTV Encoder Boxes support multiple simultaneous destinations. For YouTube Live or Facebook Live, select RTMP protocol and enter the platform’s server URL and stream key. For custom IPTV servers, use RTMP, UDP, or RTP protocols with your server’s IP address and port. VLC makes an excellent test destination—set encoder to UDP output, specify your computer’s IP and port 5004, then open network stream udp://@:5004.
Pro Tip: Configure multiple stream outputs as backup redundancy. Primary stream to main platform, secondary lower-bitrate stream to backup server protects against outages.
Step 4: Optimize Bitrate, Codec, and Resolution
For most live video broadcasting, 1920×1080 at 30fps provides excellent quality with broad compatibility. Sports benefit from 60fps, while 720p at 30fps offers good quality with reduced bandwidth. YouTube recommends 4,500-9,000 Kbps for 1080p30. Start conservatively and increase if quality is insufficient. Monitor your upload connection—encoder bitrate should not exceed 80% of sustained upload capacity.
Choose Constant Bitrate (CBR) for live streaming as it provides predictable bandwidth usage. Set keyframe interval to 2 seconds (60 frames for 30fps, 120 for 60fps) for optimal platform compatibility.
Pro Tip: Use H.265 encoding when bandwidth is limited for 40-50% savings while maintaining quality, but verify platform and device support.
Step 5: Go Live and Monitor Stream Health
Press Start to initiate streaming. Most devices display status indicators confirming connection. Allow 10-15 seconds for stabilization. Monitor dropped frames indicating bandwidth issues, network packet loss (above 0.5% requires investigation), and temperature readings. Review logs periodically to identify intermittent issues.
Pro Tip: Always test your complete workflow during off-hours before critical content. Run full-duration test streams to verify stable performance under extended operation.
Performance & Streaming Quality Benchmarks
Entry-level IPTV Encoder Box models ($150-$300) typically support 1080p at 30fps or 720p at 60fps. Mid-range models ($400-$800) handle 1080p at 60fps with some offering 4K at 30fps. Professional units ($1,200+) deliver 4K at 60fps with H.265 encoding.
Professional IPTV hardware offers bitrate adjustment from 500 Kbps for mobile streaming to 50 Mbps for near-lossless 4K. Glass-to-glass latency varies by protocol: UDP and RTP multicast deliver 500ms to 2 seconds, RTMP introduces 5-12 seconds, HLS historically 20-30 seconds though Low-Latency HLS reduces this to 2-6 seconds, and SRT balances low latency (1-3 seconds) with error correction.
Quality encoders support multiple audio inputs including embedded HDMI audio, balanced XLR microphone inputs, and line-level connections. AAC audio codec at 128-192 Kbps provides excellent quality for most applications.
Better Alternatives & Add-Ons for IPTV Encoder Box
If bandwidth costs concern you or you’re streaming 4K content, upgrading to H.265-capable IPTV Encoder Box delivers substantial savings. A 4K stream requiring 25-35 Mbps with H.264 can be delivered at 12-18 Mbps with H.265 while maintaining quality. For IPTV resellers serving bandwidth-constrained regions, this means more channels within available bandwidth.
IPTV resellers operating multiple channels should consider multi-channel encoder boxes processing 2, 4, or 8 independent sources in one device. These consolidated units reduce equipment costs, simplify network configuration, and minimize rack space versus deploying individual encoders.
Complex productions with multiple audio sources benefit from external audio embedding modules. Churches using wireless microphones, choir microphones, and instruments need quality mixing before the encoder. Professional audio embedders provide delay adjustment to compensate for video processing latency, maintaining lip-sync accuracy.
Industry-Specific Recommendations: IPTV resellers should invest in multi-channel encoders with remote management prioritizing reliability. Churches need ease of use with preset configurations and excellent audio. Esports requires low-latency streaming, 60fps minimum, SDI inputs. Hotels need multi-channel encoders with hotel management integration. Live events need portable encoders with batteries and bonded cellular streaming.
Real-World Deployment Use Cases
A regional IPTV service provider operates 50 channels serving 10,000 subscribers. By deploying multi-channel IPTV Encoder Boxes, they replaced eight individual PCs with each 8-channel encoder, reducing power consumption 75%, eliminating software licensing, and improving reliability from 94% to 99.8% uptime.
A high school athletic department streams games to parents using an IPTV Encoder Box with SDI input connected to broadcast cameras. They stream to YouTube Live and a paid platform generating $15,000 annually, recouping their $800 encoder investment in six months through subscriptions.
A 500-member congregation streams weekly services to homebound members worldwide. Their IPTV Encoder Box accepts HDMI from a video switcher mixing three cameras with audio from the church sound system. Volunteers arrive 10 minutes early, verify levels, and stream reaches 200 weekly viewers across four continents.
A boutique hotel implemented IPTV delivering 30 channels to 75 rooms via Ethernet. Using multi-channel IPTV Encoder Boxes, they transcode satellite television and custom content into IP streams accessed through smart TVs, eliminating set-top boxes and simplifying maintenance.
A university broadcasts lectures across campus using 15 IPTV Encoder Boxes in lecture halls capturing AV system content and streaming to their video platform. The solution scaled to 5,000 concurrent viewers during major events while IT manages all encoders centrally.

Common IPTV Encoder Box Mistakes to Avoid
Selecting inappropriate protocols causes compatibility issues. UDP multicast fails for internet streaming as multicast doesn’t traverse public networks—use RTMP for platform streaming, UDP/RTP for local multicast, HLS for adaptive bitrate, and SRT for resilient internet transmission.
Setting bitrate too high creates unstable streams. Your IPTV Encoder Box bitrate must not exceed 75-80% of sustained upload capacity. Connections advertising 10 Mbps may sustain only 7-8 Mbps under continuous load. Configure conservatively and verify stability before increasing.
Running outdated firmware leaves encoders vulnerable to known issues. Check for updates monthly and apply during maintenance windows. Test updates beforehand and maintain backups of working firmware versions. Most professional encoders support configuration export for quick restoration.
Inadequate network infrastructure undermines performance. Connecting encoders to congested segments causes packet loss. Implement VLANs to isolate streaming protocol traffic, configure QoS to prioritize encoder packets, and use gigabit switches. Deploy redundant network paths for critical applications.
Viewers tolerate moderate video degradation but are highly sensitive to audio issues. Ensure proper audio level adjustment—too quiet forces volume increases, too loud introduces distortion. Use balanced XLR connections to minimize interference and verify lip-sync accuracy within 100ms.
IPTV Encoder Box devices generate substantial heat. Ensure adequate clearance for airflow, avoid stacking without rack spacing, and maintain ambient temperature below 30°C. Clean vents quarterly to prevent dust restricting cooling.
Maintenance & Long-Term Care Tips
Dust accumulation restricts cooling airflow causing IPTV Encoder Box devices to overheat and throttle performance. Monthly, power down and use compressed air to clear vents. Replace external fan filters if your model includes them—$5 filters prevent expensive replacements.
Store backup encoders in climate-controlled environments. Humidity causes corrosion while temperature extremes stress components. Protect stored encoders in antistatic bags and sealed containers. Before deploying, allow gradual temperature adjustment to prevent condensation.
Establish quarterly firmware review schedules checking manufacturers’ sites for updates. Read release notes carefully to understand addressed issues. Test updates on non-critical backup encoders before production deployment. Maintain firmware archives with known-working versions enabling quick rollback.
Export encoder configurations after settings changes and store securely. Configuration backups enable rapid recovery from device failures or corruption. Document customizations not captured in exports like network firewall rules. For complex deployments, maintain configuration management databases tracking each device’s settings and service history.

Quarterly, verify cable connections remain secure and inspect for physical damage. HDMI cables are fragile at connectors—replace worn cables before failures. Verify network connections achieve gigabit speeds using encoder statistics. Test backup power supplies and UPS systems.
Review encoder logs monthly identifying patterns indicating developing problems. Increasing errors or temperature warnings signal issues requiring preventive action. Track stream statistics including bitrate, dropped frames, and connection reliability over time addressing declining metrics proactively.
Conclusion
The IPTV Encoder Box stands as an essential cornerstone of modern broadcasting infrastructure, transforming raw video signals into professional-quality streams with unmatched reliability and performance. Whether you’re an IPTV reseller managing channels, a church reaching global congregations, a hotel enhancing guest experiences, or a live event producer, dedicated encoding hardware delivers stability, quality, and scalability that software solutions cannot match.
Ready to upgrade your IPTV broadcast? Try an IPTV Encoder Box today and experience smoother, more reliable streaming. Share your setup in the comments or subscribe for more IPTV gear guides and tutorials.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between an IPTV Encoder Box and a transcoder?
An encoder converts raw video into streamable format, while a transcoder modifies existing streams by changing bitrate or resolution. Encoders create streams from original sources; transcoders adapt existing streams for different delivery scenarios.
Q2: Can one IPTV Encoder Box stream to multiple platforms at once?
Yes, many models support multi-streaming to YouTube, Facebook Live, and custom RTMP servers simultaneously. Entry-level models may support single output while professional units offer 4-8 simultaneous outputs.
Q3: Do IPTV Encoder Boxes support 4K streaming?
High-end IPTV Encoder Box models support 4K (3840×2160) streaming, typically at 30fps and sometimes 60fps. However, 4K streaming requires substantial bandwidth—20-50 Mbps depending on compression—and many platforms have limited 4K support. For most IPTV applications, 1080p H.264 encoding remains practical, offering excellent quality with manageable bandwidth and universal device compatibility. Consider 4K only when your distribution infrastructure and viewer devices genuinely benefit from increased resolution.
Q4: How much internet bandwidth do I need for my IPTV Encoder Box?
Required bandwidth depends on encoding settings. For 720p streaming, allocate 3-5 Mbps upload bandwidth. For 1080p at 30fps, you need 5-8 Mbps, while 1080p at 60fps requires 7-12 Mbps. 4K streaming demands 20-50 Mbps. These represent stream bitrate; ensure your connection’s sustained upload capacity exceeds stream bitrate by 25% to maintain stability. Test under load as advertised speeds often differ from sustained performance.
Q5: Can I use an IPTV Encoder Box for recorded content or only live streams?
While IPTV Encoder Boxes are optimized for live streaming, many models support recording encoded streams to internal storage, USB drives, or network-attached storage. This allows simultaneous broadcast and archived copy creation. Some encoders accept pre-recorded video files as input, functioning as file-based transcoders. However, for extensive recorded content workflows, dedicated transcoding software may offer more advanced file management than hardware encoders.
Maximizing Your IPTV Encoder Box Investment:
To maximize return on your IPTV Encoder Box investment, start with proper planning assessing current and future needs including channels, concurrent streams, resolution requirements, and platforms. Document network infrastructure including upload bandwidth, switch capacity, and QoS capabilities preventing costly mid-project upgrades.
Invest in quality supporting equipment. Use professional cameras with clean HDMI or SDI output and implement proper audio mixing. Deploy enterprise switches with IGMP snooping for multicast and PoE capability. Establish clear operating procedures with checklists for pre-stream verification, troubleshooting steps, and technical support contacts.
Monitor performance systematically tracking viewer engagement, stream health data, and bandwidth patterns. This informs optimization decisions and justifies infrastructure investments. Consider API integration possibilities enabling automation with broadcast workflow systems, content management platforms, and scheduling tools for centralized encoder fleet management.

