Introduction: The Television Revolution Is Here
Are you ready to witness the complete transformation of how we consume television content? The traditional cable and satellite TV model that dominated for decades is rapidly crumbling under the weight of innovation, convenience, and consumer demand for flexibility. With over 1.1 billion households expected to adopt Internet Protocol Television by 2027, the shift toward IP-based streaming is no longer a trend—it’s a revolution.
IPTV Trends are reshaping the entire digital media landscape, offering unprecedented control over what we watch, when we watch it, and how we experience content. From 4K and 8K streaming quality to AI-powered content recommendations, the future of television is being written in real-time through adaptive bitrate streaming, cloud-based infrastructure, and OTT platforms that eliminate the limitations of traditional broadcasting. IPTV Trends.
The challenges with conventional cable TV are well-documented: inflexible packages, expensive monthly fees, limited mobility, and outdated technology. Meanwhile, IPTV streaming services are delivering live TV streaming, comprehensive video on demand (VOD) libraries, and multi-device compatibility at a fraction of the cost. As broadband infrastructure improves globally and 5G networks expand, the barriers to IPTV adoption continue to disappear. IPTV Trends.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore seven powerful insights into IPTV Trends that are driving the industry forward, examine how modern IPTV systems work, compare performance benchmarks, and provide actionable recommendations for choosing the right IPTV solution for your needs.
Evolution of IPTV Technology: From Cable to Cloud
The journey of Internet Protocol Television represents one of the most significant technological shifts in media consumption history. A decade ago, IPTV was a niche technology available only to early adopters with high-speed internet connections. Today, it’s a mainstream solution powering everything from household entertainment to enterprise digital signage. IPTV Trends.
The evolution began with the transition from analog cable TV to digital broadcasting, but the real transformation occurred when content delivery shifted from dedicated cable infrastructure to IP-based networks. This fundamental change enabled streaming over existing internet connections, eliminating the need for specialized hardware beyond the home network. IPTV Trends.
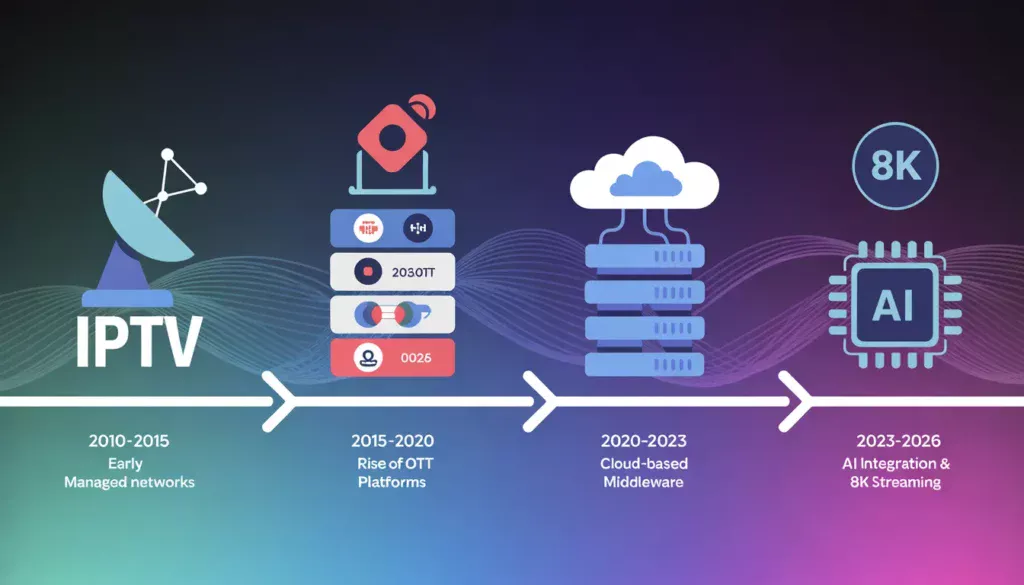
Key Milestones in IPTV Evolution:
- 2010-2015: Early IPTV deployments focused on managed networks by telecom providers
- 2015-2020: Rise of OTT platforms and unmanaged IPTV services
- 2020-2023: Cloud-based IPTV middleware becomes the industry standard
- 2023-Present: AI integration, 4K/8K streaming, and adaptive bitrate streaming dominate
The role of broadband infrastructure cannot be overstated. Fiber-optic networks delivering symmetrical gigabit speeds have made buffer-free 4K streaming commonplace. The emergence of 5G wireless technology is further democratizing access, enabling mobile IPTV streaming with minimal latency and exceptional reliability.
Modern IPTV systems leverage sophisticated encoding technologies like H.265 (HEVC) and AV1 codec to deliver superior picture quality while minimizing bandwidth consumption. These advances, combined with content delivery networks (CDNs) strategically positioned globally, ensure that IPTV Trends continue to favor the consumer with better performance and lower costs.
Key IPTV Trends Shaping the Industry in 2026
Understanding current IPTV Trends is essential for anyone looking to invest in streaming technology, whether as a consumer, reseller, or service provider. Here are the most impactful developments transforming the IPTV landscape: IPTV Trends.
Cloud-Based IPTV Platforms
The migration to cloud infrastructure represents perhaps the most significant shift in IPTV architecture. Cloud-based platforms eliminate the need for expensive on-premise servers, offering scalability, redundancy, and global reach. Providers can now spin up new channels, adjust bandwidth allocation, and implement updates without physical hardware limitations. IPTV Trends.
Benefits include automatic failover systems, geographic load balancing, and the ability to scale resources based on real-time demand. This infrastructure supports millions of concurrent viewers without degradation, something impossible with traditional broadcast technology. IPTV Trends.
AI-Driven Content Recommendations
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized content discovery in IPTV streaming services. Machine learning algorithms analyze viewing patterns, preferences, and even the time of day to suggest relevant content. These systems learn individual preferences across household members, creating personalized experiences for each user profile.
Advanced implementations now incorporate natural language processing for voice search, predictive caching that pre-loads likely content choices, and sentiment analysis from social media to recommend trending shows. This level of personalization keeps viewers engaged and reduces churn for IPTV providers. IPTV Trends.
Multi-Screen and Cross-Device Streaming
Modern consumers expect seamless content access across all their devices. Leading IPTV Trends include synchronized viewing states, allowing users to start watching on their Smart TV IPTV apps, pause, and continue on their smartphone without missing a beat.
Cloud DVR functionality syncs across devices, ensuring recorded content is accessible anywhere. This cross-device compatibility extends to features like remote scheduling, parental controls, and profile management, all synchronized in real-time through cloud-based IPTV middleware.
Interactive and Personalized Viewing Experiences
The future of IPTV isn’t passive—it’s interactive. Current trends include:
- Multi-angle viewing for sports with user-controlled camera selection
- Interactive overlays displaying statistics, player information, or shopping options
- Social viewing features enabling synchronized watch parties with friends
- Choose-your-own-adventure style content where viewers influence narrative outcomes
- Real-time polling and voting during live broadcasts
These features transform viewers from passive consumers to active participants, fundamentally changing the entertainment experience. IPTV Trends.
Step-by-Step: How Modern IPTV Systems Work
Understanding the technical workflow behind IPTV streaming services helps appreciate the complexity and sophistication of modern systems. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
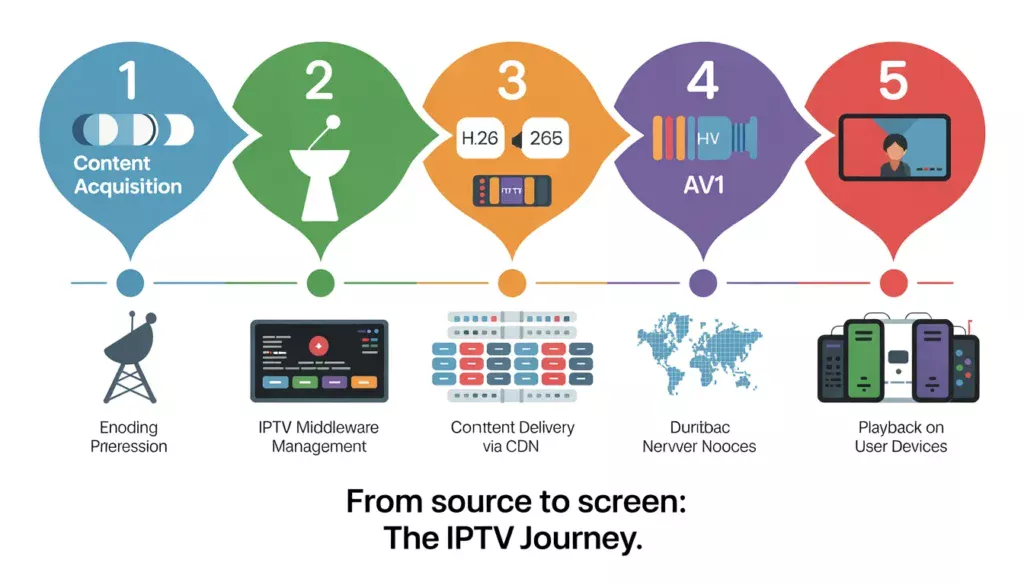
Step 1: Content Acquisition
Content originates from multiple sources: live broadcasts captured via satellite receivers, pre-recorded media from content libraries, or direct feeds from broadcasters. Modern IPTV platforms aggregate content from hundreds or thousands of sources simultaneously. IPTV Trends.
The acquisition layer includes licensing agreements, content rights management, and geographic distribution restrictions. Smart acquisition systems automatically verify content authenticity and ensure compliance with regional broadcasting regulations.
Pro Tip: Enterprise IPTV deployments should implement redundant acquisition paths to prevent single-point failures. Dual satellite receivers and multiple internet-based feeds ensure continuous operation even if one source fails. IPTV Trends.
Step 2: Encoding & Compression
Raw video content requires significant bandwidth—uncompressed 4K video can exceed 12 Gbps. Encoding converts this into manageable streams using advanced codecs. The process involves:
- Video encoding: Compressing visual data using H.264, H.265, or AV1
- Audio encoding: Processing multi-channel audio (stereo, 5.1, Atmos)
- Bitrate optimization: Creating multiple quality tiers for adaptive streaming
- Metadata integration: Adding EPG data, subtitles, and content descriptions
Modern encoding leverages GPU acceleration and cloud-based transcoding services to process content at scale. A single encoder can generate multiple output streams simultaneously, supporting various device capabilities and network conditions.
Pro Tip: Implement adaptive bitrate streaming with at least 5-7 quality tiers (from 480p to 4K) to accommodate diverse viewer bandwidth. This ensures optimal quality for each user’s connection speed. IPTV Trends.
Step 3: IPTV Middleware Management
Middleware is the brain of any IPTV operation, managing everything viewers interact with. This includes:
- User authentication and authorization
- Electronic Program Guide (EPG) management
- Subscription and billing systems
- Content recommendation engines
- Digital rights management (DRM)
- Analytics and reporting dashboards
Advanced IPTV middleware platforms integrate with CRM systems, payment gateways, and analytics platforms to provide comprehensive business intelligence. They track viewer behavior, popular content, peak usage times, and churn indicators.
Step 4: Content Delivery via CDN
Content delivery networks distribute streams geographically to minimize latency and ensure reliability. When a viewer requests content, the CDN routes the stream from the nearest edge server, dramatically reducing buffering and improving quality. IPTV Trends.
Top-tier CDN implementations include:
- Edge caching: Storing popular content closer to viewers
- Dynamic routing: Automatically selecting optimal network paths
- DDoS protection: Defending against malicious traffic
- Real-time monitoring: Detecting and resolving delivery issues instantly
Pro Tip: Choose CDN providers with significant presence in your target markets. A CDN with robust infrastructure in North America but limited presence in Asia will provide suboptimal service to Asian viewers.
Step 5: Playback on User Devices
The final step delivers content to viewers’ devices—Smart TVs, streaming boxes, smartphones, tablets, or computers. Modern playback incorporates:
- Adaptive bitrate switching: Automatically adjusting quality based on connection speed
- Buffer management: Preloading content to prevent interruptions
- Subtitle synchronization: Ensuring captions match audio precisely
- Multi-audio track support: Offering language options and audio descriptions
Smart TV IPTV apps optimize for large screens and include features like voice control, gesture navigation, and integration with smart home ecosystems. Mobile apps prioritize battery efficiency and cellular data management.
Performance & Benchmark Testing: IPTV vs Cable vs OTT
Understanding how IPTV Trends translate into real-world performance helps make informed decisions. Here’s a comprehensive comparison:
| Performance Metric | IPTV (Managed) | Cable TV | OTT Platforms | IPTV (Unmanaged) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Latency | 2-5 seconds | < 1 second | 5-15 seconds | 3-8 seconds |
| Maximum Resolution | 4K/8K | 1080p-4K | 4K HDR | 1080p-4K |
| Typical Uptime | 99.9% | 99.5% | 99.7% | 95-99% |
| Monthly Cost | $30-80 | $80-150 | $10-25/service | $15-40 |
| Channel Count | 500-5000+ | 100-300 | Limited | 1000-10000+ |
| DVR Capability | Cloud (unlimited) | Limited storage | Platform-dependent | Varies widely |
| Concurrent Streams | 3-5+ devices | 1-3 devices | 1-4 devices | 1-5+ devices |
| Internet Required | Yes (10+ Mbps) | No | Yes (5+ Mbps) | Yes (10+ Mbps) |
Real-World Performance Examples:
Scenario 1: Sports Streaming – A managed IPTV service streaming live soccer in 1080p at 60fps requires approximately 8 Mbps bandwidth and delivers smooth playback with 3-5 second delay from live broadcast. Cable TV offers near-instant playback but lacks the multi-angle viewing features available through advanced IPTV platforms. IPTV Trends.
Scenario 2: 4K Movie Streaming – IPTV streaming services delivering 4K content at 25 Mbps with HDR and Dolby Atmos provide theatrical-quality experiences. Adaptive bitrate streaming automatically downgrades to 1080p if bandwidth drops, ensuring uninterrupted viewing.
Scenario 3: Multi-Device Household – A family with 5 devices simultaneously streaming different content requires robust IPTV infrastructure. Cloud-based platforms handle this effortlessly, whereas cable TV would require multiple set-top boxes and higher subscription tiers.
Benefits Driving IPTV Adoption: Why Users Are Switching
The accelerating shift toward Internet Protocol Television is driven by tangible benefits that resonate with modern viewers. Here are the key advantages:
Benefit 1: Cost Efficiency
IPTV streaming services typically cost 40-60% less than traditional cable packages while offering more channels and features. There’s no equipment rental, no installation fees, and no regional sports fees that inflate cable bills. Month-to-month subscriptions provide flexibility without long-term contracts.
Real-World Use Case: A family paying $120/month for cable with 200 channels switched to an IPTV service offering 3,000 channels for $45/month. Including their existing internet service, they save over $900 annually while gaining access to international content previously unavailable. IPTV Trends.
Benefit 2: Content Flexibility
Video on demand libraries, catch-up TV, cloud DVR, and restart capabilities give viewers complete control. Unlike cable’s fixed schedule, IPTV platforms let users watch anything, anytime, on any device. Content libraries span decades of programming, offering nostalgia alongside current releases.
Real-World Use Case: A shift worker who misses prime-time broadcasts uses IPTV’s catch-up feature to watch news and entertainment on their schedule. The cloud DVR automatically records favorite shows, ensuring nothing is missed even during irregular work hours.
Benefit 3: Superior Streaming Quality
Modern IPTV Trends prioritize quality, with 4K and 8K streaming becoming standard for premium content. Adaptive bitrate streaming ensures optimal quality for each viewer’s connection, while advanced codecs deliver better pictures at lower bandwidth than traditional broadcasts.
Real-World Use Case: A home theater enthusiast streams 4K movies with HDR10+ and Dolby Atmos through their IPTV service, achieving picture and sound quality that surpasses cable broadcasts and rivals physical media, all without leaving their couch. IPTV Trends.

Benefit 4: Multi-Device Compatibility
Watch on Smart TVs, streaming boxes (Roku, Fire TV, Apple TV), smartphones, tablets, laptops, or desktop computers. Content syncs across devices with features like watchlist sharing, profile management, and synchronized playback positions. This flexibility accommodates modern viewing habits.
Real-World Use Case: A commuter watches their favorite series during the train ride on their smartphone, then seamlessly continues on their living room TV when arriving home. The IPTV middleware remembers the exact position, creating a frictionless experience. IPTV Trends.
Benefit 5: Global Content Access
IPTV breaks geographical barriers, offering international channels, regional programming, and content in dozens of languages. Expats stay connected to home country broadcasts, while language learners access authentic content for immersion. Sports fans follow teams worldwide without expensive international packages. IPTV Trends.
Real-World Use Case: An immigrant family maintains cultural connections through IPTV channels from their home country, while simultaneously accessing local news and entertainment. Children benefit from educational programming in their heritage language alongside English content.
Common IPTV Mistakes to Avoid: Lessons from the Field
Even as IPTV Trends make adoption easier, certain pitfalls can compromise your experience. Here’s what to watch for:
Mistake 1: Choosing Unreliable IPTV Providers
Not all IPTV services are created equal. Some operate with questionable legality, offering suspiciously cheap access to premium content without proper licensing. These services frequently experience downtime, channel removals, and potential legal consequences for users. IPTV Trends.
Solution: Research providers thoroughly. Look for established companies with transparent business practices, customer support, clear terms of service, and verifiable licensing. Read reviews from multiple sources and test services with short-term subscriptions before committing.
Pro Tip: Legitimate IPTV providers will clearly state their content licensing and geographic restrictions. If a service claims to offer every premium channel worldwide for $10/month, it’s almost certainly unauthorized. IPTV Trends.
Mistake 2: Ignoring Bandwidth Requirements
IPTV demands stable, adequate internet bandwidth. Attempting to stream 4K content on a 10 Mbps connection results in constant buffering and quality degradation. Household bandwidth must accommodate all simultaneous internet activities, not just IPTV.
Solution: Calculate total bandwidth needs: 4K streaming requires 25+ Mbps, 1080p needs 8-10 Mbps, and 720p requires 5 Mbps. Add bandwidth for other devices and activities. Upgrade internet plans accordingly and use wired Ethernet connections for primary viewing devices when possible.
Pro Tip: Test your actual internet speed during peak viewing hours, not just advertised speeds. ISPs may throttle during high-demand periods, affecting IPTV performance. Tools like Speedtest.net provide real-world measurements. IPTV Trends.
Mistake 3: Using Unsecured IPTV Apps
Downloading IPTV applications from unofficial sources poses security risks. Modified apps may contain malware, collect personal data, or provide ISPs and copyright holders visibility into viewing habits. Device security and privacy are compromised.
Solution: Only download IPTV apps from official sources—Google Play Store, Apple App Store, Amazon App Store, or directly from verified IPTV providers. Enable device security features and use VPN services if privacy is a concern, though be aware of potential legal implications.
Pro Tip: Implement IPTV security and encryption practices, including using services that support HTTPS streaming, avoiding apps requesting unnecessary device permissions, and regularly updating all software to patch vulnerabilities.
Mistake 4: Overlooking Device Compatibility
Not all IPTV services work on all devices. Some providers offer limited app support, forcing users to awkward workarounds. Additionally, older devices may lack processing power for 4K streaming or modern codec support.
Solution: Verify device compatibility before subscribing. Check if your Smart TV model, streaming box, or mobile devices support the provider’s apps. Consider future-proofing with devices supporting the latest standards (4K, HDR, Dolby Vision, AV1 codec). IPTV Trends.
Pro Tip: For maximum compatibility and performance, dedicated Android-based streaming boxes often provide the best IPTV experience, offering more flexibility than Smart TV apps and better performance than smartphone casting.
IPTV Device & Service Recommendations: Finding Your Perfect Match
Choosing the right hardware significantly impacts your IPTV experience. Here are recommendations across price tiers:
Entry-Level ($30–$60)
Amazon Fire TV Stick 4K
- Key Features: 4K HDR, Dolby Atmos, Alexa voice control, extensive app support
- Ideal For: Budget-conscious users, single TV households, casual viewers
- IPTV Compatibility: Excellent app availability, supports sideloading for additional services
Roku Express 4K+
- Key Features: 4K streaming, simple interface, thousands of channels
- Ideal For: Non-technical users, those prioritizing ease of use
- IPTV Compatibility: Good for mainstream IPTV apps, limited sideloading options
Mid-Range ($60–$120)
NVIDIA Shield TV
- Key Features: AI upscaling to 4K, gaming capabilities, Google Assistant, Plex server
- Ideal For: Tech enthusiasts, gamers, home media server operators
- IPTV Compatibility: Outstanding performance, supports all apps and formats
Apple TV 4K (3rd Gen)
- Key Features: A15 Bionic chip, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, seamless iOS integration
- Ideal For: Apple ecosystem users, quality-focused viewers
- IPTV Compatibility: Excellent app support, premium build quality
Formuler Z11 Pro Max
- Key Features: IPTV-optimized, MyTVOnline 3 app, built-in VPN, dual-band WiFi
- Ideal For: Dedicated IPTV users, international content consumers
- IPTV Compatibility: Purpose-built for IPTV with advanced features
Performance Tier ($120+)
Custom Android TV Box (High-End)
- Key Features: Amlogic S928X processor, 4GB RAM, 8K support, customizable firmware
- Ideal For: Power users, multi-room deployments, maximum customization
- IPTV Compatibility: Ultimate flexibility, supports all services and configurations
Professional Set-Top Boxes
- Key Features: Enterprise-grade reliability, dedicated IPTV middleware support, advanced troubleshooting
- Ideal For: Commercial deployments, hospitality industry, resellers
- IPTV Compatibility: Designed specifically for IPTV environments
Pro Tip: Regardless of tier, prioritize devices with Ethernet ports for stable connectivity, adequate storage for app installations, and regular firmware updates for security and compatibility improvements.
IPTV Deployment Use Cases: Real-World Applications
IPTV Trends extend far beyond home entertainment, transforming multiple industries and use cases:
Home Entertainment
The primary IPTV market remains residential entertainment. Families appreciate unlimited content options, personalized viewing experiences, and cost savings. Multi-room viewing with synchronized accounts, parental controls for children’s safety, and integration with smart home systems create comprehensive entertainment ecosystems. IPTV Trends.
Key Benefits: Substantial cost reduction compared to cable, access to international programming, flexibility to add or remove services without penalty, and future-proof technology that adapts to changing viewing habits.
Sports Streaming
Live TV streaming has revolutionized sports consumption. IPTV platforms offer multiple viewing angles, real-time statistics, interactive betting integration, and social features. International sports previously unavailable through cable are now accessible, while DVR functionality ensures fans never miss crucial moments.
Key Benefits: Access to global sporting events, multi-angle viewing for enhanced experiences, pause and rewind capabilities during live broadcasts, and lower costs than traditional sports cable packages.
Hospitality & Hotels
The hospitality industry has rapidly adopted IPTV for guest room entertainment. Hotels deploy IPTV systems offering guests personalized content, language options, streaming service integration, and billing to room charges. Systems also display hotel information, services, and local attractions.
Key Benefits: Enhanced guest satisfaction through modern entertainment options, reduced hardware costs compared to traditional systems, easy content updates and customization, and revenue opportunities through premium content offerings. IPTV Trends.
Businesses and Digital Signage
Corporate environments use IPTV for internal communications, training content distribution, and digital signage. Retail stores display promotional content, restaurants show menus and specials, and offices broadcast company news and announcements across multiple locations simultaneously.
Key Benefits: Centralized content management across multiple locations, real-time updates and scheduling, cost-effective compared to traditional signage, and integration with corporate communication systems.
Maintenance & Long-Term Reliability: Ensuring Optimal Performance
Maximizing your investment in IPTV streaming services requires ongoing attention to maintenance and optimization:
Regular App Updates
IPTV apps receive frequent updates addressing security vulnerabilities, adding features, and improving compatibility. Enable automatic updates on devices or check weekly for new versions. Outdated apps may experience playback issues, security risks, or incompatibility with service updates.
Best Practice: Schedule monthly reviews of all installed IPTV applications, removing unused services and ensuring current versions are installed. Many playback issues resolve simply by updating to the latest app version. IPTV Trends.
Network Optimization Tips
Network performance directly impacts IPTV quality. Implement these optimizations:
- Use wired Ethernet connections for primary viewing devices to eliminate WiFi instability
- Configure Quality of Service (QoS) on routers to prioritize streaming traffic
- Separate IoT devices onto guest networks to prevent bandwidth competition
- Upgrade router firmware regularly for security and performance improvements
- Position WiFi routers centrally and away from interference sources (microwaves, cordless phones)
- Consider mesh WiFi systems for large homes requiring comprehensive coverage
Best Practice: Run speed tests regularly at different times to identify bandwidth bottlenecks or ISP throttling. Document baseline performance for troubleshooting future issues.
Security Best Practices
Protecting your IPTV investment and personal data requires attention to security:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all IPTV accounts and middleware logins
- Enable two-factor authentication where available
- Keep devices updated with the latest security patches
- Use reputable VPN services if privacy is a concern, understanding potential legal implications
- Avoid sharing account credentials even with trusted individuals
- Monitor account activity for unauthorized access or unusual viewing patterns
Best Practice: Implement network-level security through router firewalls, DNS filtering services, and regular security audits of connected devices.
Backup and Redundancy Strategies
Serious IPTV users implement backup plans for uninterrupted service:
- Subscribe to multiple IPTV providers for service redundancy
- Maintain alternative internet connections (cellular hotspot, secondary ISP)
- Configure automatic failover in advanced IPTV middleware systems
- Back up device configurations for quick restoration after failures
- Document installation procedures for rapid redeployment
Best Practice: Test backup systems quarterly to ensure they function correctly when needed. Dormant backup subscriptions or untested configurations fail exactly when needed most. IPTV Trends.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Television
The IPTV Trends explored throughout this comprehensive guide represent more than technological evolution—they signify a fundamental shift in how humanity consumes media. From cloud-based infrastructure and AI-driven recommendations to 4K/8K streaming and interactive viewing experiences, Internet Protocol Television delivers everything traditional broadcasting promised but never achieved. IPTV Trends.
The benefits are undeniable: dramatic cost savings, unprecedented content flexibility, superior quality, multi-device compatibility, and global access. Whether you’re a cord-cutter seeking alternatives to expensive cable packages, a tech enthusiast embracing bleeding-edge streaming technology, or a business deploying professional IPTV solutions, the opportunities have never been more compelling.
As broadband infrastructure continues improving, 5G networks expand, and IPTV middleware becomes increasingly sophisticated, the gap between IPTV and traditional television will only widen. Early adopters are already reaping rewards, while late adopters will eventually have no choice but to join the revolution.
The key to success lies in understanding these IPTV Trends, making informed provider and device choices, implementing proper security and maintenance practices, and staying current with evolving technology. The future of television isn’t coming—it’s already here.
Explore the future of IPTV today and upgrade your streaming experience. Whether starting your IPTV journey or optimizing an existing setup, the knowledge and recommendations in this guide provide the foundation for success. The only question remaining: Are you ready to cut the cord and embrace the future?
FAQs: Your IPTV Questions Answered
Q1: What are the most important IPTV trends today?
The most significant IPTV trends in 2026 include cloud-based platform migration for scalability and reliability, AI-driven content recommendations providing personalized viewing experiences, adaptive bitrate streaming ensuring optimal quality across varying bandwidth conditions, multi-device synchronization allowing seamless viewing across all screens, and the integration of 4K/8K streaming with advanced codecs like AV1. Additionally, interactive viewing features, enhanced security through encryption, and the proliferation of OTT platforms are transforming how consumers access and experience content.
Q2: Is IPTV better than cable TV?
IPTV offers several advantages over traditional cable TV, including significantly lower costs (typically 40-60% less), vastly more channel options (often thousands versus hundreds), superior flexibility with on-demand content and cloud DVR, multi-device compatibility allowing viewing anywhere, and access to international programming. However, IPTV requires stable high-speed internet (10+ Mbps minimum) and may experience slightly higher latency during live broadcasts. For most users prioritizing cost, flexibility, and content variety, IPTV represents the superior choice, though cable TV still offers advantages in sports latency and doesn’t depend on internet connectivity. IPTV Trends.
Q3: Are IPTV services legal?
IPTV technology itself is completely legal. Many legitimate IPTV services operate with proper content licensing, including major providers like YouTube TV, Hulu + Live TV, Sling TV, and telecom-provided IPTV services. However, some IPTV services offer copyrighted content without authorization, operating in legal gray areas or outright illegally. To ensure you’re using legal IPTV services, verify that providers have transparent business practices, clear terms of service, proper content licensing, and reasonable pricing that reflects content acquisition costs. Extremely cheap services offering premium content worldwide are typically unauthorized and pose legal risks.
Q4: What internet speed is required for IPTV?
Internet speed requirements for IPTV depend on streaming quality and the number of simultaneous streams. For standard definition (SD), minimum 3-5 Mbps is required. For 720p HD streaming, you need 5-8 Mbps. For 1080p Full HD, plan for 8-10 Mbps. For 4K Ultra HD streaming, you need 25-35 Mbps per stream. For multiple concurrent streams, multiply these requirements by the number of simultaneous viewers and add bandwidth for other household internet activities. For optimal IPTV performance, internet speeds should be at least 25% higher than minimum requirements to account for fluctuations. Wired Ethernet connections provide better stability than WiFi, especially for 4K content.

